Glad to know that you have generated assets more than enough, thanks to the biggest obsessions of Indian investors towards real estate and gold. Many people are not acquainted about wealth tax, it is the less famous sibling of income tax, which is payable on the wealth accumulated by individuals over the years. As it is an additional tax, to be levied over and above income tax.
While income tax is payable on the total taxable income earned by an individual in one year, wealth tax is paid on the possession of certain assets which fall under the purview of the Wealth Tax Act of the Indian taxation system.
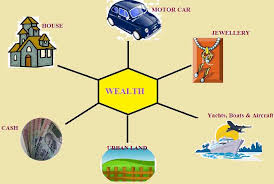
Prescribed Assets as Wealth
Like individual’s income tax, wealth tax is also determined by one’s nationality such as residential status and location of wealth assets. If an individual has acquired Indian national and resident as per Income tax laws, he will have to pay wealth tax in India, even on global assets. Basically, the intention of the law is to tax assets that do not generate an income means unproductive or ideal assets. It includes certain prescribed assets such as building or land, motor cars, gold and silver coins, precious stones, jewellery, bullions, yachts, boats and aircraft, urban land, even cash in hand etc.
However, productive and financial assets, such as commercial property, bonds, fixed deposits, stocks, Ulips, gold funds, mutual funds, your savings account bank balance and gold exchange traded funds (ETFs) are not included for computing one’s net wealth because they are produced an income and liable to pay tax thereon as per prescribed slabs.
Valuation of Assets
The value of taxable assets for the purpose of wealth tax would be their value as on the last day of the respective financial year that is as on 31st March of the tax year. Further, such value of assets except cash will have to be determined in accordance with the valuation norms laid down in the Wealth Tax Act. For instance, urban land, cars, yachts, boats and aircraft, valuation shall be based on a fair market value, or FMV. It is best to have an approved valuer decide the FMV as the assessing officer might reject the estimates that have been prepared by you. In determining the value of the assets, the outstanding loans taken to buy in respect of assets are reduced from the value of the assets, whether bought, gifted or inherited.
Exemptions and Clubbing Provisions
There are some exemptions that are available with respect to certain prescribed assets. For example, one house of an individual/ HUF or on a plot of land which does not exceed 500 square meters, neither any residential property that is let out for a minimum of 300 days in the relevant previous year, nor on any property which is held for business purposes. Motor cars that are held by an assessee for running them on hire or held as stock in trade are also not included in your wealth. The same applies to jewellery that is held as stock in trade for the purpose of business. And the any cash in locker or at home not exceeding Rs50,000 is kept to exempt from the definition of wealth assets.
Clubbing provisions similar to that in the Income-tax Act exist in the wealth tax Act. For instance, if you transfer assets to your spouse or son’s wife or to any person under a revocable transfer or to a person for the benefit of either without adequate consideration as gift, the value of assets that was transferred must be added to your net wealth for taxation purpose.
How much Wealth Tax do you pay?
Once you have identified and the value of your net assets—that is asset less any liability such as loans relating to the assets. It is to be considered on the valuation date, which is the last day of the fiscal year i.e. 31st March. You will have to pay only 1% of the net value of taxable wealth assets if it exceeds Rs30 lakh as on the valuation date for the financial year.
What should be your Action Plan?
Given the above facts and provisions, your action plan is to check if you are liable to pay wealth tax or not, if so, get to prepare a list of all assets and investments owned by the family and then, classify the assets based on the legal ownership, assets purchased by own funds, gifts and inheritance. The next step is to compare the assets listing with the definition of assets under the wealth tax Act.
Once you have the above data ready, you will need to compute your wealth tax liability and also examine the various exemptions available under wealth tax provisions.
Let us take an example. Ankur Jain has a residential house property worth Rs 1.50 crore on which there is an outstanding loan of Rs 80 lakh, motor car worth Rs 16 lakh, gold jewellery Rs 45 lakh and cash in hand of Rs 3.50lakh. For the purpose of wealth tax, we will first need to calculate Jain’s total wealth.
Jain’s net wealth works out to be Rs 34 lakh as aggregate of Rs 64 lakh for gold jewellery, motor car and cash in hand minus Rs 30 lakh. And he is liable to pay wealth tax worth Rs 34,000 only, i.e. 1% of Rs34 lakh
A self-occupied residential house or a plot of land that does not exceed 500 square meters is exempt from wealth tax.
Implications for not Paying Wealth Tax
The repercussions of not filing wealth tax return or any declaration of wealth made is incorrect, its implications may be very harsh as revenue authorities can impose a penalty of up to 500 per cent of the amount of tax evaded. In cases of willful default or the tax evaded exceeds Rs1 lakh , imprisonment of up to seven years could also be imposed. If you fail to pay wealth tax on due date, you will have to add 1% interest on the tax for every month on delay. There is also provision to impose a penalty for delay in filing wealth tax return; it can be Rs100-200 per day.
Since the consequences could be very rigorous, it is best to understand the definition of wealth and the compliance requirements for an individual. You may consider taking professional help to understand the liability under the wealth tax Act. This can also help you to keep a track of your wealth tax liability for future purchases or investments.
Suresh Kumar Narula is founder and Principal Financial Planner at Prudent Financial Planners. He has earned the professional CERITIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER and got registered with SEBI as Investment Advisor. He writes on personal and financial planning articles and got published in Dainik Bhaskar, Business Bhaskar and The Financial Planner’s Guild, India. He is also a member of Financial Planner’s Guild India ( An association of practicing SEBI registered Investment advisers) to create awareness about Financial Planning in general public, promote professional excellence and ensure high quality practice standards. Suresh received his an M.com from Himachal Pardesh University and an MFC from Punjab University, Chandigarh. He can be reached at info@prudentfp.in

gucci sale India
Yes, I like it.
Thanks for the same.
Sites we Like…
[…] Every once in a while we choose blogs that we read. Listed here are the latest sites that we choose […]…
Its my pleasure.